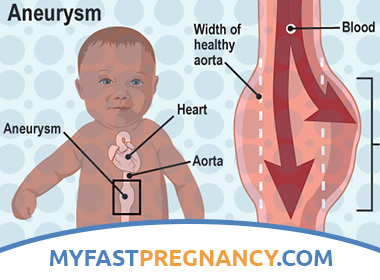
What is Aneurysm in Children?
Aneurysm in children – protrusion of the walls of blood vessels, heart, veins, arteries due to thinning or stretching of the tissue. Cases of vein aneurysm are rare. Due to the stretching of the walls of the artery, a bag is formed, which can put pressure on neighboring organs, making it difficult for them to function normally, and can also break – this situation is a threat to the child’s life.
In infants and young children, aneurysm can be asymptomatic for many years. Identify it in such cases when conducting x-ray or ultrasound. Also, the disease can be manifested by complaints of pain or tingling in the problem area. Aneurysm in children can be congenital or acquired.
Acquired aneurysm is the result of severe injuries, tumors and injuries, infection, syphilis, hypertension, etc.
Aneurysm Forms:
- Cerebral artery aneurysm
This aneurysm prevents normal blood flow and brain activity. There is a violation of motor activity, headache, epileptic seizures, impaired sensitivity. Mortality ranges from 10 to 30%. - Aortic aneurysm
This is a common pathology of the aortic wall, representing a danger to the lives of children and adolescents. The cause may be trauma, syphilis, atherosclerosis. There is pain behind the sternum, tightness in the chest, shortness of breath, dry, painful cough (when squeezing the trachea and bronchi). A child may also have hoarseness and difficulty in swallowing with this form of aneurysm. If the aortic aneurysm is torn, it is almost always fatal. - Aneurysm of the heart
In this form, the thinned and non-functioning heart wall protrudes. The reason is the pathology of internal development, which can be detected by ultrasound, when the child is still in the womb. The work of the heart is disturbed, which is manifested by signs of heart failure. There is a risk of rupture, which entails a lethal outcome.
Causes of Aneurysm in Children
There are many causes of aneurysm in children. As noted above, the aneurysm can be congenital, or appears in the process of child development. This may be a congenital weakness of the connective tissue. At risk are children who have aneurysm among their relatives. Also at risk are people with a genetic connective tissue disease called Marfan syndrome.
The appearance of the aneurysm is affected by diseases that weaken the elasticity of the vascular walls:
- late stage syphilis
- atherosclerosis
- vasculitis
- hypertension
Against cystic medial necrosis, the development of dissecting aortic aneurysm may occur. At the same time, through a small gap in the inner lining of the vessel, blood penetrates into its middle layer. Hypertension in children without adequate treatment and control of blood pressure can cause aneurysm.
Smoking in adolescents is an important risk factor, it accelerates the growth of the aneurysm, and also causes hypertension and atherosclerosis. If we talk not only about children, but about the entire population as a whole, smokers are 4 times more likely to suffer from aortic aneurysm compared with non-smokers.
Aneurysms can also be associated with vascular injuries or the formation of infected blood clots. Blood clots mostly settle in small vessels. Infection of them is transmitted to the vessel wall, which causes pathology. Aneurysms as a consequence of injury are more common in adolescents than in small children. At risk – those who got into an accident and teenagers who like extreme sports.
Pathogenesis during Aneurysm in Children
According to the mechanism of development, aortic aneurysms are divided into true, false and dissecting. True associated with the violation of the structure of the aortic wall. With a pronounced atheromatosis of the aorta with atrophic and destructive changes in the middle shell, the prerequisites for the expansion of the aorta in the form of its diffuse aneurysm are created.
Syphilitic aneurysms are the result of a syphilitic mesaortitis. Injuries cause false aneurysms. In peri-or para-aortic hematoma, fibrin is compacted and organized, a fibrous wall with cellular infiltrates is formed. Later, the development of elastic fibers, the growth of the inner membrane and endothelium, lining the bag mainly near the “neck” of the aneurysm in a child.
If we talk about pathomorphology, aneurysms are divided into diffuse and limited. Diffuse are a significant expansion of the aortic lumen (length is different), sometimes they reach 10 cm. The shape is cylindrical or spindle-shaped. And limited aneurysms in children look like a limited protrusion of a saccular, scaphoid or funnel-shaped form, the magnitude of which may be different. The inlet has the same diameter as the aneurysm, or narrower. Often the inner surface is covered with tubercles (hyperplastic changes, atheromatosis), blood clots.
Symptoms in aneurysm occur due to compression of nearby organs. The brightness of the symptoms depends on the size and location of the aneurysm. Depending on the location, systolic murmur is heard above the aorta. With a significant aneurysm to the right of the sternum in the II-III intercostal space, the dullness of the percussion sound is determined, a pulsation is noticeable.
The pressure of the aneurysm on the branches of the vagus nerve leads to bradycardia. Aneurysm of the aortic arch can cause narrowing of the brachial head, left carotid and subclavian arteries. In such cases, on the affected side, the pulse is greatly weakened or even inaudible. This is especially pronounced when the hands of the child are raised upwards. Aneurysm of this localization reveals paralysis of the left vocal cords. The compression of the bronchus can cause lung atelectasis with the development of pneumonia in the future. The pressure on the left cervical sympathetic node causes Horner’s triad: exophthalmos, anisocoria, narrowing of the palpebral fissure.
Aneurysm of the descending aorta is almost always caused by syphilis. It compresses the esophagus and the cardiac part of the stomach, which leads to dyspeptic symptoms, dysphagia, etc. Stenosis of the renal arteries in some cases may manifest symptomatic arterial hypertension.
Aneurysm of the abdominal aorta squeezes the abdominal organs. There is persistent pain in the epigastric region and lower back in the later stages of the disease. The compression of the ureters causes anuria. Squeezing of the renal arteries causes symptomatic hypertension. When squeezed by a duodenal aneurysm, phenomena similar to pylorospasm appear.
Complicated aortic aneurysms in children are a breakthrough in the superior vena cava, pleural cavity, trachea and esophagus, retroperitoneal tissue, abdominal cavity, inferior vena cava, intestines. A tampon hematoma is formed, then a hemorrhage into the cavity occurs, collapse occurs, and then death.
Symptoms of Aneurysm in Children
Aneurysm of the aorta of the thoracic in children
Symptoms may not appear. If they appear, then in the area in which the aortic curvature is concentrated downwards. Often the child has pain in the chest area, which older children characterize as aching and deep. Typical symptoms also:
- dyspnea
- cough
- backache
- pain when swallowing
- snore
Aortic aneurysm abdominal
When this type of aneurysm appears spilled pain in the abdominal region, discomfort variable or permanent nature. There may be pain in the sides, chest, lower back. They are sometimes distributed to other departments. It can hurt for 2-3 hours and even 3-4 days. When the motor activity pain does not change. But in some positions of the body the pain may increase. A typical symptom is pulsation in the abdomen.
When the aortic aneurysm of the abdominal cavity can be blue or darkening of the fingers, pain in them, cold feet. These symptoms occur when thrombi form during aneurysm, which block or partially block blood flow to the extremities. Symptoms include fever and weight loss, if the aneurysm is manifested by inflammatory processes.
These symptoms in this and another type of aneurysm appear the less, the smaller the child’s age. The symptoms of aneurysm in adolescents are similar to those in adults, and in young children the aneurysm is often asymptomatic, wherever it is located.
Aortic aneurysm rupture in children and adolescents
These symptoms appear:
- sharp decline in blood pressure
- acute, sharp pain in the chest or abdomen
- respiratory disorders
- tachycardia
- blueness or paleness of the skin
- lack of ability to move and answer questions
- lack of response to pain
In the absence of rapid medical care comes the death.
Diagnosis of Aneurysm in Children
It is very difficult to diagnose aortic aneurysm by only one manifestation; special studies are required. X-rays can be used to diagnose the aneurysm of the thoracic aorta. At multiaxial X-ray examination, the pulsating shadow of the aneurysm, inseparable from the aorta, is clearly visible.
In some cases, they do not only roentgenoscopy and chest X-rays in various projections, but also pneumomediastinography and tomography. An important diagnostic method is scanning of the aorta using different contrasts, for example, iodine-131-bilignost, etc. In some cases, aortography is performed.
Differential diagnosis of aneurysm in children
Aneurysms of various parts of the aorta during diagnosis are distinguished from tumors, including malignant tumors, from cancer:
- mediastinum
- easy
- guts
- stomach
The prognosis for aortic aneurysms is unfavorable in most cases.
Treatment of Aneurysm in Children
Therapy of aneurysm in children depends on the growth rate and its size. With a large and rapidly progressing aneurysm, surgical treatment is necessary. In such cases, the replacement of the damaged area of the blood vessel with an artificial graft is mainly done. Small aneurysms rupture in very rare cases. For their treatment, they use mainly the same drugs as with high blood pressure, as well as drugs that help reduce the load on the aortic wall.
If an operation was previously performed, patients should periodically have an ultrasound scan to monitor the state of the aneurysm. If the aneurysm does not grow and predictably does not rupture, there is still the risk of heart problems in the child. In such cases, you need a diet and a healthy diet and exercise. Teenagers are strongly recommended to quit smoking. Doctors may prescribe medications to lower blood cholesterol levels.
Prevention of Aneurysm in Children
If the aneurysm is congenital, preventive measures are meaningless. But the acquired aneurysm can be prevented. Teens should not smoke, it is detrimental to the state of the heart and blood vessels. Blood pressure should be monitored if there are any problems with it. The child must eat balanced, healthy foods. It is recommended to exclude dishes with trans fats and convenience foods, to temper the amount of sweets. In the diet should prevail vegetables, fruits, unrefined carbohydrates.
The child should engage in physical exercise or sports. Negative impact on the condition of the blood vessels and the heart. If you have such a problem, try to revise the diet of the child or take him to an endocrinologist. Make sure that the height and weight of the child progressed proportionally. Children and adolescents for the prevention of aneurysm should sleep more than 7 hours a day and avoid stress.