What is Allergic Diathesis in Children?
Allergic diathesis is an increased sensitivity of the body to the food consumed, which occurs as a result of the innate characteristics of the immune system, the neurovegetative system, and the metabolism.
Diathesis is associated with the peculiarities of the child’s body, diathesis in adults is extremely rare. In children, food is digested differently than in adults, the body responds differently to infectious pathogens, etc. That is, those factors that do not cause a reaction in an adult organism can affect the child’s organism.
The hyperactive immune response given by the child’s body to environmental antigens causes skin inflammation and other effects. According to statistics, diathesis is observed in 1/3 of children, because this disease is considered to be common in pediatric practice.
There are several types of diathesis. Among them – allergic diathesis in children. It is found, as a rule, between the ages of 3 and 6 months. The disease persists for 1-2 years, later disappears in most children. The child, while still in the womb, may feel the effects of allergens that enter the mother’s body. Allergens are transmitted to infants during breastfeeding and as a result of complementary feeding.
Causes of Allergic Diathesis in Children
Allergic diathesis in children is a disease that is genetically transmitted (hereditary). It is also formed due to the characteristics of the immunological protection and enzyme formation of the child’s body, and as a result of the influence of the external environment.
The risk factor is, first of all, the development of the fetus inside the womb. The fetus is affected by poor maternal nutrition and toxicosis. Allergic diathesis can be the result of damage to the central nervous system during labor or fetal hypoxia. Influencing, infectiousness and massive drug therapy affect the development of the disease. Characteristically, bottle-feeding is also a cause of diathesis. Babies who are breastfed are 5-7 times less likely to suffer from allergic diathesis.
A typical source of allergens is food that has not been cooked:
- raw milk
- eggnog
- whipped berries
Products that have undergone heat treatment, but have retained their allergenic properties, for example, fish, nuts, cause diathesis. The cause of the diathesis is ordinary foods if the child eats them in excess. For example, diathesis may occur if the diet of a child for the most part consists of dairy products: yogurt, milk, sweet cheeses.
If the child has some foods rarely, but in large quantities, allergic diathesis may also occur. For example, these are berries that come once a season. You can not give the child and products that are not laid on age: shrimp, caviar, etc. Risk factors are also the abuse of sweets (desserts), irrational and chaotic food, excessive amounts of spicy and salty in the diet. Also, the disease may occur if in a short time to enter into the diet of the child a lot of new products. Thus, the child develops an allergy not only to food, but also to dust, wool, etc.
Pathogenesis During Allergic Diathesis in Children
Forms of diathesis may be immune and nonimmune. To the first form belongs the transient and true diathesis. These two options are based on the overproduction of immunoglobulins E (IgE) and a decrease in IgA, IgG and T-lymphocyte levels. A transient variant occurs when cow’s milk antigen enters the bloodstream, while excess IgE production is secondary.
Antigenemia is the result of insufficient albumin digestion due to the deficiency or low activity of specific enzymes and increased gastrointestinal permeability to protein in young children. Babies up to 6 months have a low immunological barrier of the intestines, which is associated with a very small amount of SlgA in the mucosa. Secretory immunoglobulin is in breast milk, so when breastfeeding a baby, its deficiency is covered.
The antigen, while in the child’s blood, provokes an overproduction of IgE. The same reaction may occur on drugs, vaccinations, baby cosmetics, household chemicals, and so on. Antigenemia not all children manifested as diathesis. In the pathogenesis of an important failure of the tissue barriers of the child. In the body, there may be a deficiency of blocking antibodies, which leads to the free formation and fixation of haptens in the skin and mucous membranes. Reagin sensitization develops.
Further, local mast cell degranulation occurs. Biological active substances are released. Vascular permeability increases, exudative reactions occur. In a minority of cases, the true immune genesis is at the core of allergic diathesis. IgE overproduction is inherited, manifested when an antigen enters the body. This form can develop into allergic diseases.
An important part of the pathogenesis is neuroendocrine and metabolic disorders. Often diathesis occurs in children with posthypoxic encephalopathies. It is believed that hypoxic states can provoke endocrine disorders, which manifest themselves in most cases of discorticism.
Symptoms of Allergic Diathesis in Children
Pallor, pastos of children with allergic diathesis are noted. Body weight increases unevenly, and easily decreases with diseases. See the friability and hydrophilic subcutaneous tissue. Often it is over-developed. Lowered tissue turgor and skin elasticity. Observe the pronounced phenomena of paratopia.
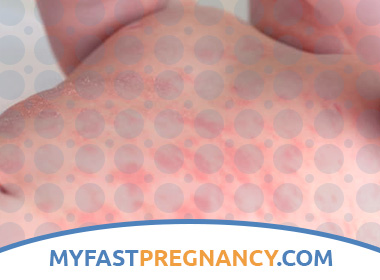
Manifestations of diathesis on the skin occur in children at an early age, even in the first weeks of life. The maximum is at the age of 6 to 12 months. A “gneiss” appears on the hairy parts of the head – seborrheic scales are formed, the skin flakes off. On skin folds, parents may notice diaper rash, which is greatest in the perineum and on the buttocks.
Later, these symptoms appear:
- cheek skin infiltration
- hyperemia of the skin of the cheeks
- peeling of skin on cheeks
- strophulus
Combing these places, the child gets pinpoint erosion. Yellowish crusts are formed. Secondary infection may occur. In severe cases, eczema can “go” on most of the torso, arms and legs, which leads to anxiety, itching, and intoxication. The child is disturbed by sleep due to discomfort.
After a year, the child has the following symptoms:
- erythematous-papular rash
- urticaria
- pruriginous rashes
- neurodermatitis
- dry eczema
- increased desquamation of the epithelium of the tongue (some parts of the tongue swell, the epithelium peels off)
- stomatitis
- inflammatory eye disease
- upper respiratory tract diseases
A child can easily have blepharitis, conjunctivitis, pharyngitis, recurrent rhinitis, bronchitis, sinusitis, false croup. The asthmatic component is not excluded. The course of the disease is often severe, there are pronounced disorders of microcirculation, toxicosis, eksikoz.
In allergic diathesis, children may have changes in the urine: leukocyturia, proteinuria, flat epithelial cells. It is not excluded dysfunction of the intestine, which is manifested in rapid, mucous-thinned stools. In children from 1 year old, the asthma component often turns into bronchial asthma, biliary tract dyskinesia and gastrointestinal tract are typical for this age.
Allergic diathesis in children is also manifested by hyperplasia of lymphadenoid tissue, which is considered secondary. Tonsils and adenoids are enlarged, as is the liver, spleen, lymph nodes.
Diagnosis of Allergic Diathesis in Children
For diagnostic use laboratory methods. Eosinophilia is increasing, which speaks of allergization. Protein, fat, carbohydrate metabolism is violated. This can be seen in the reduction of albumin and gamma-globulins, hypo-and dysproteinemia, amino acid imbalance, hypocholesterolemia, high initial sugar level. The balance of acids and bases shifts towards acidosis.
Also, allergic diathesis is primarily diagnosed by external manifestations, such as characteristic changes in the skin and mucous membranes, hyperplasia of lymphadenoid tissue. Doctors also note the phenomenon of paratrophy. The child’s body is less resistant to infectious diseases.
Treatment of Allergic Diathesis in Children
Based on the obtained diagnostic data, doctors develop a special diet for the child. We must strictly adhere to the recommendations of the doctor! Apply the ointment without a doctor’s prescription is strictly contraindicated, because what you can take for diathesis, can be a manifestation of more serious diseases.
Doctors may prescribe a means to relieve itching, strengthen the immune system. As a local treatment, doctors prescribe ointments and lotions. The baby is made baths with a string, oak bark, potassium permanganate, celandine, etc.
Forecast
When eliminating allergens in a child’s life and keeping a special diet for two or three years, enzyme and immune systems differentiate, increase the barrier functions of the skin and mucous membranes, stabilize metabolic processes. Only in some children (mainly with a true immune form of the disease and unfavorable living conditions) does allergic diathesis become allergic diseases such as eczema, neurodermatitis, and bronchial asthma.
Prevention of Allergic Diathesis in Children
Prevention of allergic diathesis can be carried out when the child is not yet born. Infectious diseases of the mother and the use of drugs during the gestation period should be avoided. A pregnant woman should eat properly and regularly, try to avoid a monotonous diet. During breastfeeding, the diet should be particularly diverse.
If your child has or has diathesis, it is better to take a test for food allergens to find out what products he should not give.